Introduction In the dynamic and margin-pressured world of modern healthcare, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a fringe experiment—it is a critical investment. However, for every CEO and COO managing a healthcare organization, the imperative remains the same: demonstrate a clear, quantifiable Return on Investment (ROI). Automating operations with AI for the sake of automation […]

Introduction
In today's digital landscape, automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses aiming to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and reduce labor time. This blog post delves into the various types of automation technologies that can revolutionize administrative tasks, offering real-world use cases and outlining the unique benefits of each.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
What It Is: RPA uses software robots or AI workers to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks.
Use Cases:
- Invoice Processing: Extract data from invoices, input it into a database, and send a confirmation email to the supplier.
- Employee Onboarding: Automate the process of gathering new employee documents, setting up email accounts, and enrolling them in benefits.
- Data Migration: Move data from legacy systems to new platforms without manual intervention.
Benefits:
- Time Efficiency: Drastically reduces time spent on repetitive tasks.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes the risk of human errors.
- Increased Productivity: Allows employees to focus on more strategic tasks.

Business Process Automation (BPA)
What It Is: BPA focuses on the technology-enabled automation of complex business processes.
Use Cases:
- Hiring Process: Automate job ad postings, resume screening, and interview scheduling.
- Customer Onboarding: Streamline the process of welcoming new customers, from account setup to initial engagement.
- Inventory Management: Automate the tracking and reordering of stock levels.
Benefits:
- Streamlined Processes: Makes complex processes more efficient.
- Improved Service Quality: Enhances customer and employee experiences.
- Cost Reduction: Lowers operational costs through efficiency.
IT Process Automation (ITPA)
What It Is: ITPA links disparate systems and software to make them self-acting or self-regulating.
Use Cases:
- System Monitoring: Automatically restart servers and notify the IT team when issues arise.
- Patch Management: Automate the process of updating software across multiple systems.
- Backup and Recovery: Automate data backups and enable quick recovery in case of data loss.
Benefits:
- System Reliability: Increases uptime and system stability.
- Reduced Downtime: Minimizes outages and disruptions.
- Resource Allocation: Frees up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
Advanced Automation Technologies
AI and Machine Learning (ML)
What It Is: AI and ML automate complex tasks requiring decision-making capabilities.
Use Cases:
- Customer Service: Automate email responses to common queries.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use machine learning to predict when machinery is likely to fail.
- Fraud Detection: Implement AI algorithms to detect fraudulent activities in real-time.
Benefits:
- Complex Task Automation: Capable of automating tasks that require decision-making.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Provides more personalized and efficient customer interactions.
- Data-Driven Insights: Analyzes large datasets to provide actionable insights.
Workflow Automation
What It Is: A designed sequence of tasks governed by business rules.
Use Cases:
- Content Approval: Automate the process of approving and publishing content.
- Expense Reporting: Streamline the submission and approval of expense reports.
- Sales Funnel Management: Automate the process of moving leads through the sales funnel.
Benefits:
- Process Streamlining: Makes workflows more efficient.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes the chance of human errors.
- Improved Collaboration: Enhances team coordination and communication.
Software-Defined Automation
What It Is: Automates tasks in software development and IT operations.
Use Cases:
- Code Deployment: Automate the process of deploying new code to production.
- Environment Setup: Automate the provisioning and setup of development environments.
- Quality Assurance: Automate testing processes to ensure software quality.
Benefits:
- Speed: Accelerates the software development cycle.
- Reliability: Ensures consistent and error-free deployments.
- Resource Optimization: Allows developers to focus on coding rather than operational tasks.
Specialized Automation Tools
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants

What It Is: Automate tasks like customer service and meeting scheduling.
Use Cases:
- Customer Service: Answer frequently asked questions on a company's website.
- Meeting Scheduling: Automate the process of scheduling meetings based on availability.
- Order Processing: Assist in automating the order placement and tracking process.
Benefits:
- 24/7 Customer Service: Provides round-the-clock customer interaction.
- Reduced Workload: Lightens the load on customer service staff.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Offers quick and accurate responses.
Data Automation
What It Is: Automates data manipulation, analysis, and reporting.
Use Cases:
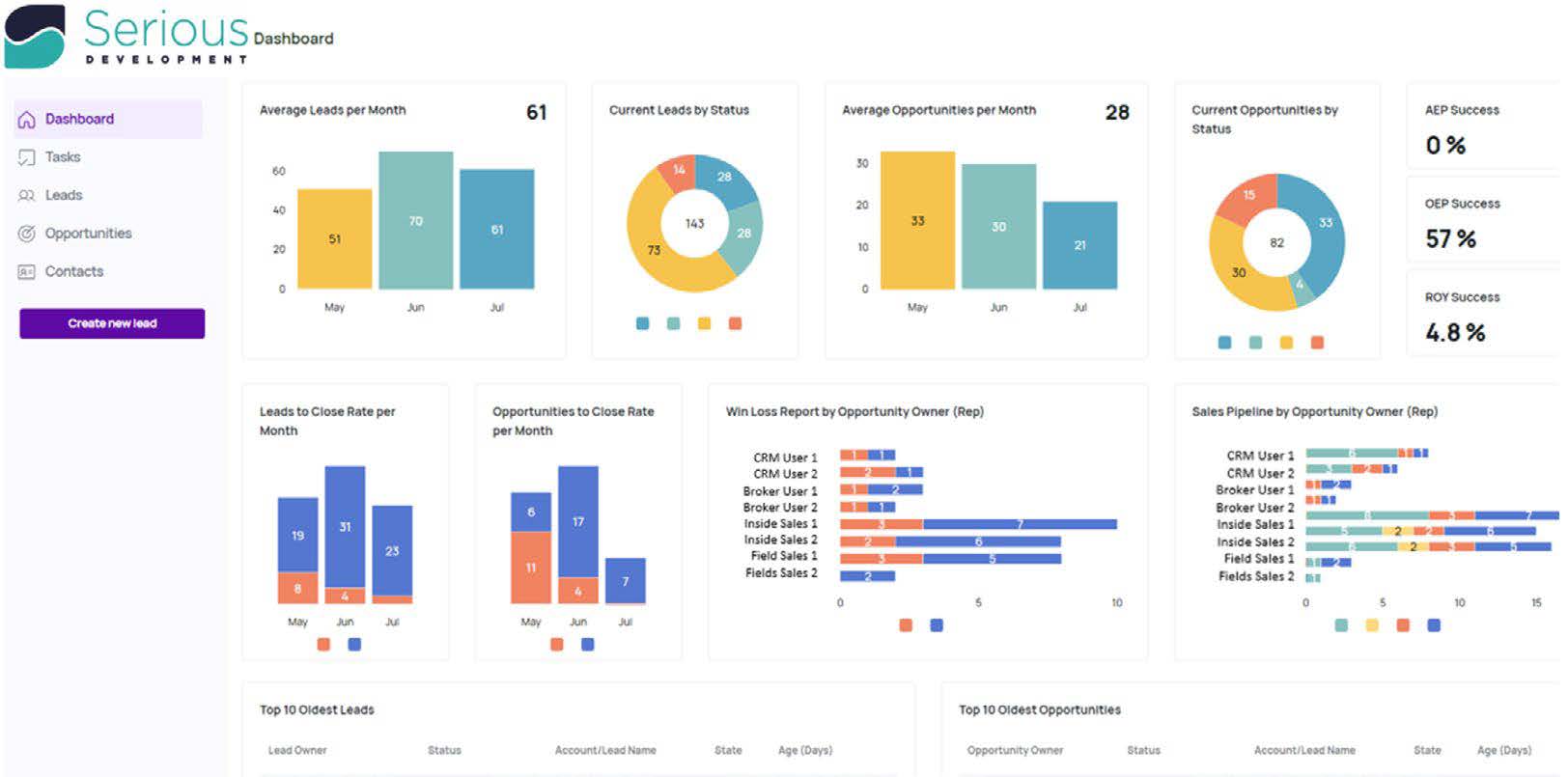
- Sales Reporting: Automate the generation and distribution of sales reports.
- Data Cleaning: Automate the process of cleaning and formatting raw data.
- Real-Time Analytics: Provide real-time insights based on incoming data.
Benefits:
- Accuracy: Enhances the reliability of data analysis.
- Real-Time Insights: Offers up-to-date data for decision-making.
- Time-Saving: Reduces the manual effort required for data manipulation.
Email Automation
What It Is: Automates tasks like newsletter distribution and email list management.
Use Cases:
- Newsletter Distribution: Automatically send out newsletters at specified times.
- Drip Campaigns: Automate a series of emails sent out based on user behavior.
- Customer Retention: Automate follow-up emails for customer engagement.
Benefits:
- Efficiency: Streamlines the email marketing process.
- Customer Engagement: Increases open rates and customer interaction.
- Reduced Human Error: Minimizes the risk of sending incorrect or duplicate emails.
Scripting and Macros
What It Is: Scripting languages and macros can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks.
Use Cases:
- File Management: Automate the process of moving files from one location to another. For example, at the end of each day, a script could automatically move all files from a user's desktop to a backup server.
- Data Scraping: Use scripts to automatically scrape data from websites for analysis or reporting. This can be particularly useful for market research or competitive analysis.
- Automated Reporting: Create macros in spreadsheet software like Excel to automatically generate reports from raw data, saving hours of manual work.
Benefits:
- Versatility: Capable of automating a wide range of tasks, from simple to complex.
- Productivity Boost: Reduces the time spent on repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Error Minimization: By automating tasks, the risk of human error is significantly reduced, leading to more accurate results.
Conclusion
Automation is an invaluable asset for businesses aiming to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and propel growth. By carefully selecting the right automation tools that align with your specific needs, you can achieve remarkable improvements in both efficiency and productivity.
But implementing automation isn't just about the technology; it's also about having the right partner to guide you. At Serious Development, we specialize in not only implementing these automation solutions but also in identifying untapped opportunities for automation within your organization. In fact, it's not uncommon for us to spot these opportunities while we're actively working with you on other projects. Our expertise ensures that you're not just automating but optimizing.
Ready to take the next step in your automation journey? Contact Serious Development today to discover the best automation solutions tailored for your business.






